PG LAB (CS509)
Assignment 2
For this programming assignment, you are required to implement external sorting with the N-way merge algorithm.
Dataset creation:
For this question, you would have to create a synthetic table (simulating sales records of department stores) containing 50000 records. Each record in this file contains four fields:
- Transaction ID (an integer): to identify each transaction uniquely in the dataset.You can create this field using a simple “counter” in your code.
- Transaction sale amount(an integer): a random integer between 1 and 60000.
- Customer name (string): a random 3 letter string.You can model this as a character array of length 3.
- Category of item: a random integer between 1 and 1500.
After creating this dataset, you need to simulate its storage on a disk.
Define a disk block as a file which can store only B records of the synthetic table.
Assume an unspanned organization i.e., records are not allowed to span across two disk blocks.
Following this store your entire synthetic table as a collection of these “disk blocks.”
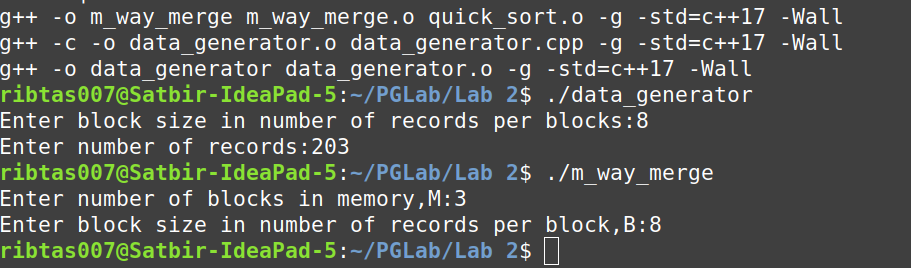
Each disk block (simulated as a file) should have a unique name, for that you can name them as 1.txt, 2.txt, 3.txt, ..., etc.
Basically, your original synthetic sales table would be stored as a series of files. For e.g., if B=300, then
the first disk block (file) would store Row 1 -- Row 300;
the second disk block (second file) would store Row 301 – Row 600.
Do not hard code the value of B. It may be changed during the evaluation.
For sake of simplicity use text files for simulating the disk blocks. Also note that each disk block should have an entry at its end which stores the file name of the next disk block for the file.
Additionally, in your code you should store the file name of the first disk block of the synthetic sales table. This would be needed at a later stage to perform a linear scan through the file.
You need to sort the file on the transaction sale amount.
Note: all the intermediate runs (created during the sort process) should be managed/stored as “simulated disk blocks” only.
Finally, your code should produce a txt file as output which contains the records in the sorted order.
Details of Simulated Main Memory:
Assume that you have space for storing only M “simulated disk blocks” in the main memory. In other words, you are allowed to read/operate on a maximum of M “simulated disk blocks” at a time.
Do not hard code the value of M. It may be changed during the evaluation.
Evaluation details:
We will have following major test cases:
- Can the code dynamically change the order of merge (merging 2, 3, 4..M-1 runs) depending on the value of M given? Partial points will be given if the order of merge is hard coded to 2.
- Small dataset test case: Here, we will give you a small dataset (e.g., 20 records, B=1 M=3) (or ask you to create this small dataset) to test the correctness of your code.
- Large dataset test case: For this, we will test the code on the 50,000 records dataset to see the scalability aspects of your code. We may also change B and M values accordingly. Make sure your code is robust to these kinds of changes.
Solution